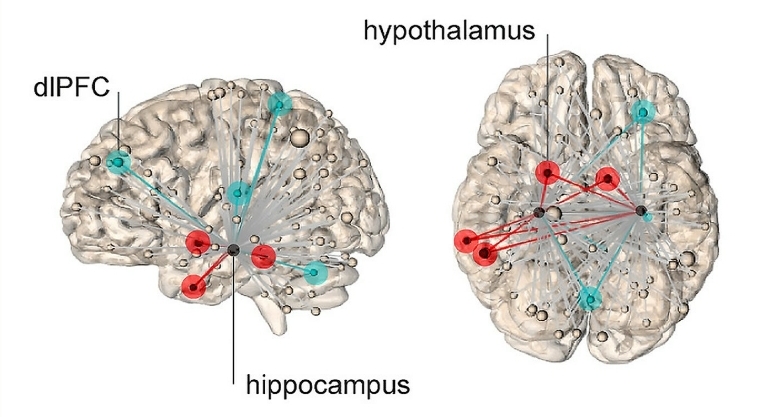
Researchers have identified activity in a hippocampal neural network that activates during stress, while connectivity between the hippocampus and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex predicts less stress.
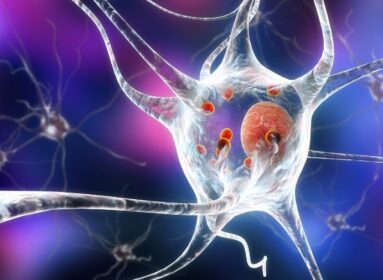
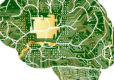
The blue lines represent connections to dorsal lateral frontal cortex, and lower subjective
levels of stress. Image is credited to Yale.
Yale researchers have found a neural home of the feeling of stress people experience, an insight that may help people deal with the debilitating sense of fear and anxiety that stress can evoke, Yale researchers reported recently in the journal Nature Communications.
Brain scans of people exposed to highly stressful and troubling images — such as a snarling dog, mutilated faces or filthy toilets — reveal a network of neural connections emanating throughout the brain from the hippocampus, an area of the brain that helps regulate motivation, emotion and memory.
The brain networks that support the physiological response to stress have been well studied in animals. Activation of brain areas such as the hypothalamus triggers production of steroid hormones called glucocorticoids in the face of stress and threats. But the source of the subjective experience of stress experienced by people during the COVID-19 pandemic, for instance, has been more difficult to pinpoint.
“We can’t ask rats how they are feeling,” said Elizabeth Goldfarb, associate research scientist at the Yale Stress Center and lead author of the study.
Goldfarb and co-authors, including senior author Rajita Sinha, the Foundations Fund Professor of Psychiatry, conducted a series of fMRI scans of subjects who were asked to quantify their stress levels when presented with troubling images.
The study reveals that neural connections emanating from the hippocampus when viewing these images reached not only areas of the brain associated with physiological stress responses, but also the dorsal lateral frontal cortex, an area of the brain involved in higher cognitive functions and regulation of emotions. The Yale team found that when neural connections between the hippocampus and frontal cortex were stronger, subjects reported feeling less stressed by the troublesome images.
Conversely, subjects reported feeling more stressed when the neural network between the hippocampus and hypothalamus was more active.
The authors note there is also evidence from other studies that those suffering from mental health disorders such as anxiety may have difficulty receiving calming feedback from the frontal cortex in times of stress.
The sensation of stress is generated by neural networks emanating from the hippocampus. Networks represented by red lines show connections to hypothalamus, which predict higher levels of stress.
“These findings may help us tailor therapeutic intervention to multiple targets, such as increasing the strength of the connections from the hippocampus to the frontal cortex or decreasing the signaling to the physiological stress centers,” said Sinha, who is also a professor in Yale’s Child Study Center and neuroscience department.
All study subjects were healthy, she said, and in some cases their responses during the experiment seemed to be adaptive — in other words, the network connections with the frontal cortex became stronger as the subjects were exposed to the stressful images. Sinha and Goldfarb speculated that these subjects might be accessing memories that help moderate their response to stressful images.
“Similar to recent findings that remembering positive experiences can lower the body’s stress response, our work suggests that memory-related brain networks can be harnessed to create a more resilient emotional response to stress,” Goldfarb said.
Although the feeling of stress is ubiquitous, the neural mechanisms underlying this affective experience remain unclear. Here, we investigate functional hippocampal connectivity throughout the brain during an acute stressor and use machine learning to demonstrate that these networks can specifically predict the subjective feeling of stress. During a stressor, hippocampal connectivity with a network including the hypothalamus (known to regulate physiological stress) predicts feeling more stressed, whereas connectivity with regions such as dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (associated with emotion regulation) predicts less stress.
These networks do not predict a subjective state unrelated to stress, and a nonhippocampal network does not predict subjective stress. Hippocampal networks are consistent, specific to the construct of subjective stress, and broadly informative across measures of subjective stress. This approach provides opportunities for relating hypothesis-driven functional connectivity networks to clinically meaningful subjective states. Together, these results identify hippocampal networks that modulate the feeling of stress.Bottom of Form
Source: Yale University















































Comments are closed.